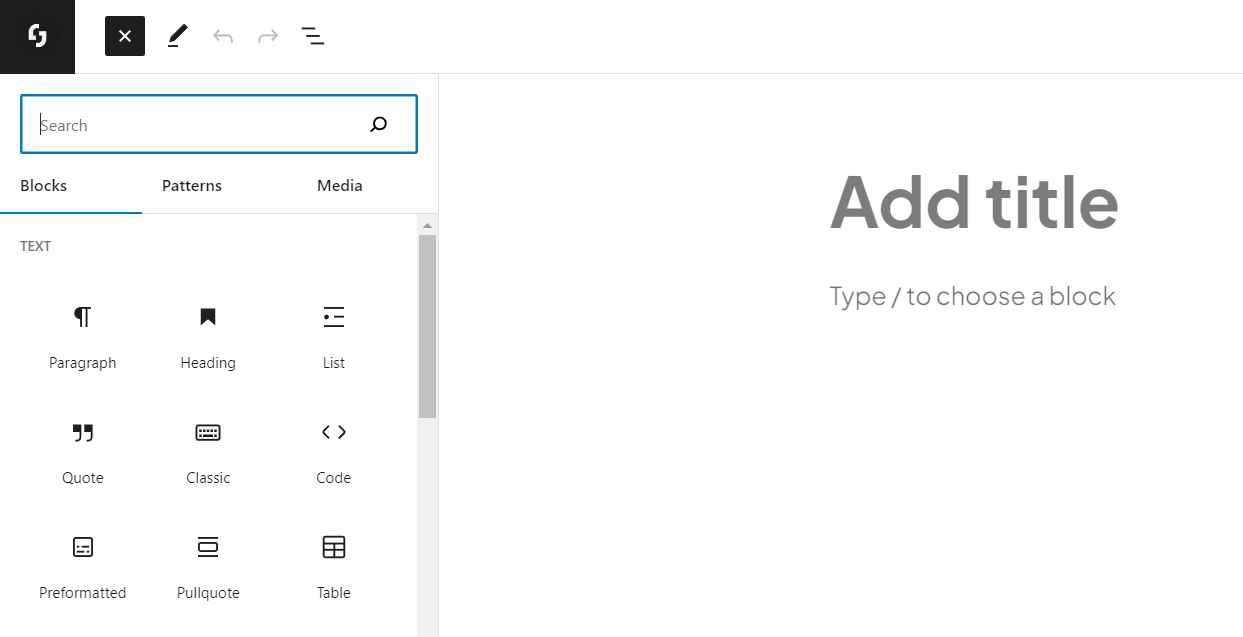
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to use the WordPress Block Editor, commonly known as Gutenberg. If you’re new to WordPress, you may find our article on What is WordPress quite helpful. Gutenberg became the default editor for WordPress 5.0 and above, introducing an entirely new way of creating content. This revolutionary editor uses a concept called ‘blocks’ to build pages and posts. This article is here to help you navigate through Gutenberg, understand its advantages, and effectively utilize its features to create engaging content.
Block Editor vs Classic Editor
Before Gutenberg, WordPress used the Classic Editor. The difference between these two lies mainly in the editing experience. The Classic Editor is a traditional text window, whereas Gutenberg introduces a modern, block-based approach to creating content. A ‘block’ can be anything – a paragraph, image, heading, or even more complex layout elements like columns or buttons.
Using Gutenberg comes with several advantages over the Classic Editor. It offers more flexibility and control over the layout, and its block-based approach makes it easier for beginners to create complex page structures without needing knowledge of code.
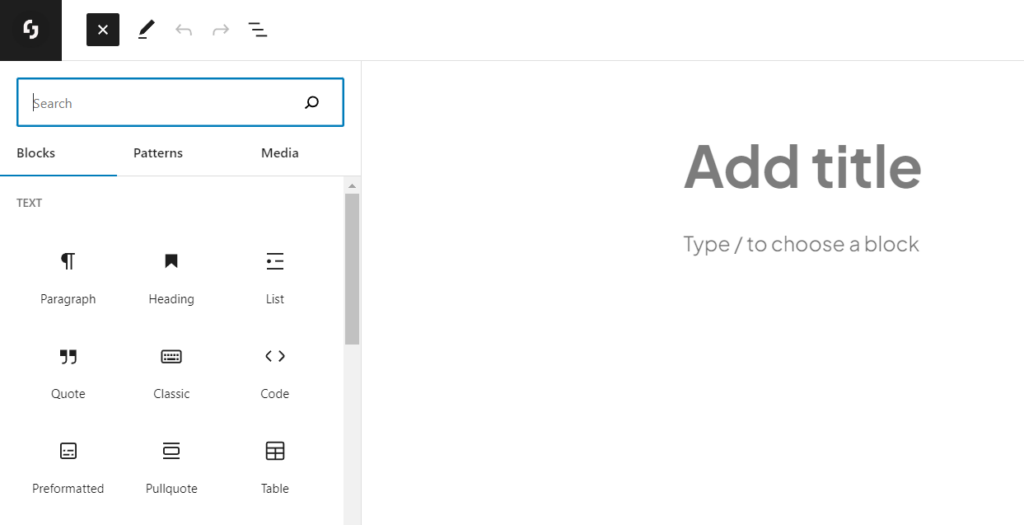
How to use Block Editor
Now, let’s delve into how to use Gutenberg. When you open the editor, you’ll see an ‘Add Block’ button on the top left corner. Click on it and select the type of block you want to add to your page or post.
There are numerous blocks available, ranging from simple text and image blocks to more complex blocks like galleries, columns, rows, and cover images. Here are some of the main blocks you will frequently use:
- Paragraph: This block is used for adding text content. It comes with options for changing text size, color, and background color.
- Heading: Use this block to add headings (H1 to H6) to your content.
- Image: This block allows you to add images to your content. You can upload images directly or select from your media library.
- List: Use this block to add bulleted or numbered lists to your content.
- Quote: This block is used for adding quotations.
- Audio: This block allows you to add an audio file or a music track.
- Cover: This block is used for adding a cover image to your post or page.
- Gallery: Use this block to add multiple images in a grid format.
- Video: This block allows you to add a video to your post or page.
- Columns: Use this block to add columns to your content. Each column can contain other blocks.
After adding a block, you can customize it using the options in the right-hand sidebar.
Pros and Cons
While Gutenberg has revolutionized content creation in WordPress, it’s not without its drawbacks. Its block-based approach can be overwhelming for users accustomed to the Classic Editor. Some users also find it less intuitive and report that it slows down their workflow.
On the other hand, Gutenberg outshines alternatives like the Classic TinyMCE editor and Page builder plugins in several aspects. It gives you a live preview of your content as you build it, which these alternatives don’t offer. Plus, Gutenberg is free, while many popular page builders are premium tools.
Here are a few popular alternatives to Gutenberg:
- Elementor: This is a drag-and-drop page builder with a wide array of features. It offers a more visual editing experience compared to Gutenberg and comes with a plethora of pre-built templates.
- Divi Builder: Divi is another popular drag-and-drop page builder. It offers advanced design features and is part of the Divi theme, though it can be used with other themes as well.
- Beaver Builder: Beaver Builder offers a frontend drag-and-drop interface and is known for its speed and ease of use.
- WPBakery Page Builder: Formerly known as Visual Composer, this page builder offers both front-end and back-end editing.
- Classic Editor: For those who prefer the traditional WordPress editing experience, the Classic Editor plugin restores the old WordPress editor and the Edit Post screen.
If you’re considering alternatives, it’s worth looking at our review of the best WordPress page builders for more options.
Extending the Block Editor
You can also extend Gutenberg’s functionality with plugins. These plugins add a variety of new blocks and design options to Gutenberg, allowing you to create more complex and attractive content. Here are a few plugins that can enhance the Gutenberg editor:
- Spectra – Ultimate Addons for Gutenberg: This plugin offers a library of unique, creative, and easy-to-use blocks to make your pages stand out.
- Stackable – Gutenberg Blocks: Stackable expands Gutenberg’s capabilities with a suite of high-quality blocks.
- CoBlocks: CoBlocks adds additional blocks and extends the existing Gutenberg blocks with more functionality.
- Kadence Blocks: This plugin offers custom blocks and options to extend Gutenberg’s editing capabilities, enabling you to create custom layouts and designs.
- EditorPlus: EditorPlus enhances the Gutenberg editor with extra typography, design, and animation features.
Remember to backup your WordPress website before installing any new plugins to prevent data loss.
Creating Custom WordPress Editor Blocks
One of the exciting features of Gutenberg is the ability to create custom blocks. Custom blocks allow you to define reusable block templates that can be added to posts or pages. This is particularly useful if you find yourself regularly adding the same content or layout to different posts or pages.
To create a custom block, you’ll need to do a little coding. First, you need to register your new block in JavaScript, then define its behavior and appearance in PHP and CSS. However, if you’re not comfortable with coding, you can use a WordPress plugin to create custom blocks. Here are several plugins that allow you to create custom blocks without writing a single line of code:
- Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) Block: This plugin allows you to create custom Gutenberg blocks using only PHP.
- Lazy Blocks: This is a Gutenberg blocks visual constructor for WordPress developers. You can create custom blocks in the admin UI without writing any code.
- Block Lab: Block Lab makes it super easy to build custom blocks. Create fields, output HTML templates, and all with a simple PHP API.
- Genesis Custom Blocks: This plugin provides a simple templating system for building custom blocks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Gutenberg block editor is a powerful tool that provides a new, flexible way of creating content in WordPress. While it has its learning curve, the benefits it brings are well worth the effort. Whether you’re building your first website or are a seasoned WordPress veteran, Gutenberg offers features and functionality that can take your content to the next level.
FAQ
What is the WordPress Gutenberg Block Editor?
The WordPress Gutenberg Block Editor, often simply called Gutenberg, is the default content editor for WordPress version 5.0 and above. It uses a block-based system for creating and organizing content, providing a more visual and intuitive way to build your WordPress posts and pages.
Can I use the Classic Editor instead of Gutenberg?
Yes, if you prefer the Classic Editor, you can install the Classic Editor plugin to replace Gutenberg. However, it’s worth noting that Gutenberg offers several advanced features not available in the Classic Editor.
How can I extend Gutenberg’s functionality?
You can extend Gutenberg’s functionality by installing plugins. Plugins like Gutenberg Blocks – Ultimate Addons for Gutenberg, Stackable – Gutenberg Blocks, CoBlocks, Kadence Blocks, and EditorPlus offer a range of additional blocks and functionalities to enhance your content creation process.
What are some alternatives to Gutenberg?
While Gutenberg is the default WordPress editor, there are several alternatives available such as Elementor, Divi Builder, Beaver Builder, and WPBakery Page Builder. These offer different features and may better suit your needs depending on your website design requirements.
How can I create custom blocks in Gutenberg?
You can create custom blocks in Gutenberg by registering your new block in JavaScript, then defining its behavior and appearance in PHP and CSS. Alternatively, you can use plugins like Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) Block, Lazy Blocks, Block Lab, and Genesis Custom Blocks to create custom blocks without coding.
Is Gutenberg better than the Classic Editor?
Gutenberg offers a more visual and flexible approach to content creation compared to the Classic Editor, making it easier to create complex layouts. However, the best choice depends on your personal preference and familiarity with each editor.
Do I need to back up my WordPress website before using Gutenberg?
It’s always a good practice to back up your WordPress website before making major changes, such as switching to a new editor like Gutenberg. This ensures you can restore your site if anything goes wrong.